What is Radiation
What is Radiation
Radiation is the result of atoms becoming unstable and emitting high-energy particles in the form of ionizing radiation. As the atom expels ionized particles, it is losing energy to stabilize its net charge. The process in which atoms release particles in order to become more stable is called radioactive decay.
Radioactive Decay
Despite what it may seem, not all ionizing radiation is in the form of nuclear radiation. Nuclear radiation is different from other types of radiation in the fact that it results due to instability from the nuclei. Lower forms of ionizing radiation like X-rays only affect the stability of electrons.
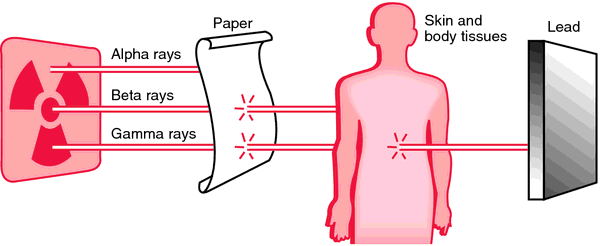
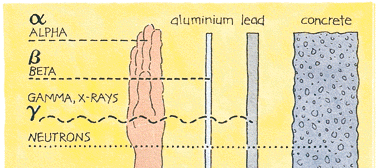
The particles expelled during radioactive decay can take on varying levels of radiation; most commonly in the form of alpha, beta and gamma. Alpha and beta radiation are weaker forms of radiation that barely penetrate the surface of most objects. Gamma is much more powerful and can only be stopped by lead or concrete. The most powerful type of radiation comes from neutrons, which can pass through everything but a thick layer of concrete.
As much as we try to protect ourselves, we are exposed to radiation everyday. Radiation is present in our environment in low doses, invisible to the naked eye. However the radiation we experience is generally not enough to cause significant harm. The most widespread form of radiation we are exposed to comes from the sun, in the form of ultraviolet rays.
Ultraviolet Radiation
Ultraviolet is a weaker form of radiation, which only affects the surface of our skin. While it can burn the skin, the radiation cannot penetrate deeper than that to cause harm to our internal organs. More harmful forms of radiation can penetrate the skin to cause damage to organs and DNA.
Nuclear Radiation
Some of the more severe types of radiation can be found in power plants. Power plants use radiation in the form of uranium, neptune and pluton to create massive amounts of energy. When a nuclear power plant generates energy, the power comes from the heat created by the ionization of atoms. Water is heated by this process and is used to turn turbines through steam power. The water also serves to cool down the reactor and prevent it from over heating. Nuclear radiation is given off as a byproduct of this process.
Prevention
Control is needed to prevent exposure to humans from radiation. Accidental exposure to radiation can cause severe damage to a person’s body, and in many cases death. While lead is effective in keeping radiation out concrete is the most effective, since it can be layered on thickly. The thicker the barrier is the less there is a chance of radiation being able to penetrate it.
http://www.duke-energy.com/about-energy/generating-electricity/nuclear-how.asp
http://www.quickanddirtytips.com/education/science/what-is-radiation
http://usmilitary.about.com/od/glossarytermsn/g/n4414.htm
http://science.howstuffworks.com/radiation3.htm
http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/radiation